
- Nematodes (belonging to the order Ascaridae), prominent representatives - roundworms, pinworms, and whipworms;
- Tapeworms or tapeworms (order Flatworms), represented by Tapeworm and Bovis;
- Flukes or trematodes (order Flatworms) are represented by liver flukes.
- Mechanical transfer involves movement over long distances, and worm development does not occur within the carrier. These include most arthropods (crustaceans, arachnids, and millipedes) and are usually carried on the legs of common flies.
- An intermediate host is a specific mode of transmission in which a developmental stage occurs within the body of the vector. For example, for the bovine tapeworm, the vector (intermediate host) is cattle, and humans are the final vector.
- Active (contact);
- Passive (food).
Worm life cycle, reproduction and development
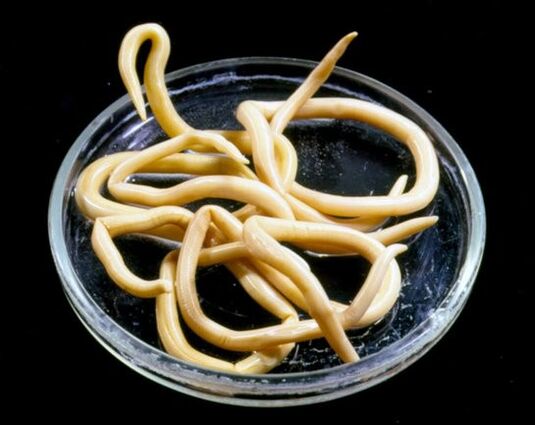


symptom
- loose (unsteady) stool;
- pain and bloating;
- allergic rash;
- flatulence;
- nausea;
- Vomit;
- Lack of or excessive appetite;
- At night - sleep disturbance, tossing and turning, teeth grinding, drooling;
- Itching of the anus;
- Mucus or blood in the stool.
- Intoxication appears almost simultaneously with infection but is not so obvious in the early stages. The higher the number of worms in a person's body, the more severe the symptoms of poisoning - from morning sickness to vomiting and abdominal pain.
- Pulmonary congestion (infiltration), bronchospasm, pneumonia. The culprit is a parasite that grows in and damages the alveoli of the lungs, triggering the inflammatory process.
- Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis). An infectious disease that results from the life activities of worms and subsequent intoxication.
- Meningoencephalitis is a dangerous inflammation of the brain and its membranes caused by bacteria and protozoa.
diagnosis
- bile research;
- Visual inspection (identifying roundworms and pinworms);
- Muscle tissue biopsy to check for trichinellosis;
- X-rays and ultrasound.
Treatment of helminthiasis
- Thoroughly disinfect the patient's sheets and the room in which he or she is located. Minimize contact and separate utensils.
- Eat a strict diet that excludes alcohol. It is recommended to drink carrot juice and birch bud infusion.
- Maintain personal hygiene, wash hands frequently, do laundry, and clean living areas.
- Monitor treatment progress and effectiveness.
- Garlic infusion enema, take garlic on an empty stomach;
- Tansy infusion, taken on an empty stomach, 4 times a day, before meals;
- Mugwort alcohol tincture, 20 mg 3 times a day.
Prevent helminthiasis
- Wash vegetables and fruits in hot water;
- Keep the house clean and wet-clean regularly;
- Eat a balanced diet to provide your body with adequate amounts of vitamins of all types;
- Monitor your pet's condition and visit your veterinarian annually;
- Proper heat treatment of fish and meat;
- Fighting Insects in the House;
- Avoid swimming and resting where cattle graze.






































