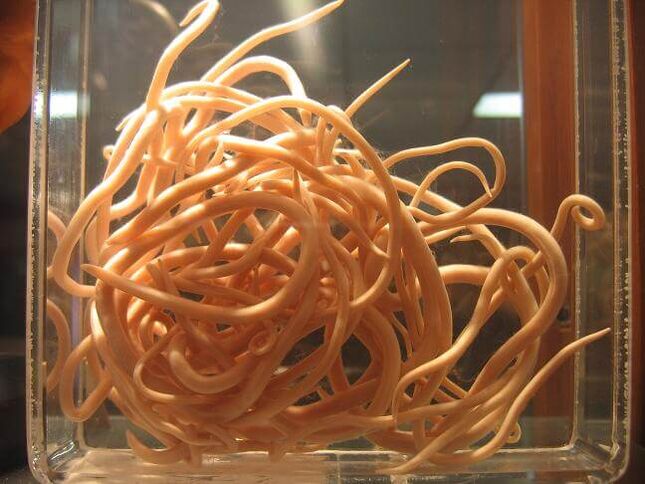

What types of worms are there?
- exposure to worms- Found only in humans, has a simple developmental cycle and does not require multiple hosts. Typical examples are pinworms; they are the most common intestinal worm in children. Infection occurs in households, children's groups, public places through unwashed hands, household items (toys, books, curtains, etc. ) contaminated with mature eggs of these worms, and inhalation of dust.
- Soil worm swarm– Their eggs must first mature in soil, water or sand. They enter the body through the mouth with unwashed berries, vegetables or herbs (such as roundworms and whipworms) or through the skin (such as hookworms).
- biological worm– Have a complex life cycle with changes in the host. These worms are acquired by eating unwashed vegetables or raw water (echinococcosis), animal meat contaminated with larvae (cattle or pork tapeworms), planed fish and caviar (leaf tapeworms), river fish (trematodes or liver flukes) or through the bloodAppears in humans (filariasis).
Type of worm
- Class Nematoda (roundworms)– Roundworms, pinworms, hookworms, whipworms, trichinella spiralis. Roundworms are characterized by the presence of different sexes and come in different sizes - from 1 cm (female pinworms) to 40 cm (roundworms).
- Class Flukes (commonly called flukes)– Siberian fluke (cat fluke), Schistosoma. They are always biological worms and hermaphrodites, equipped with various devices for suctioning and attaching to internal human organs.
- Class Taenia (types of flatworms)- These are long-banded parasites. These include the broad, pork and bovine tapeworms – the largest of the worms, reaching lengths of up to 20 metres. Flatworms feed on the entire surface of the body and are hermaphroditic and biological worms. Echinococci are considered the smallest representatives of tapeworms.
About roundworms
- Pinworm- Lives in the lower part of the human small intestine and throughout the large intestine; females lay eggs around the anus at night, causing the characteristic symptom of enterobiasis in humans - itching. Worms are spread from person to person through dirty hands (eggs of these worms are often found under children's fingernails), bedding and household items. The eggs are very light and can be spread by dust in the air; they can survive for up to six months. These are the least virulent worms. They are not found in human feces; for diagnosis, scraping from the perianal area is required.
- roundworms- A large worm with a curved hook at the end; mature individuals can reach half a meter in length. The eggs mature in the soil and pass into the stomach and small intestine along with unwashed berries, vegetables or herbs. The released larvae bite through the intestinal wall and penetrate the hepatic veins, from where they travel with the blood and rush into the lungs, the right part of the heart, and sometimes into the brain and eyes, causing inflammation of these organs. When coughing, sputum containing larvae enters the mouth and is swallowed again into the gastrointestinal tract, where it develops into mature individuals and lays eggs a month later. These worms are brown or reddish in color because they hijack red blood cells. Roundworms can live up to 2 years. For diagnosis, stool needs to be tested for eggs.
- Whipworm- A hair-thin worm about 5 cm long with a sharp end that clings to the inner surface of the intestinal wall. The eggs mature in the soil, from where they burrow into the intestines, where the larvae emerge. Whipworms feed on blood and like to stay in the cecum and appendix, often causing inflammation and anemia. Life expectancy is approximately 3-4 years. To detect it, you need to test your stool for eggs.
- Trichinella spiralis- A small round bug that moves between predators and livestock. A person becomes infected by eating meat with larvae on it; after a few days, in the intestines, mature individuals of Trichinella spiralis form and then give birth to live larvae. They can infect the entire body via the bloodstream, but they prefer skeletal muscle, where they can survive for up to 5 years.
About tapeworms and flukes
- Bull tapeworm (commonly known as tapeworm)- Considered the largest worm in humans (up to 15-20 meters long), its body is band-shaped and consists of thousands of individual segments, the most mature of which is the tail, which is shed as the eggs inside it mature. The fragments, which are about the size of a human fingernail, fall to the ground, grass and end up in cows. A person becomes infected by eating the meat of a cow. The bovine tapeworm can live in the human small intestine for up to 10 years; it feeds across the entire surface of the body. For diagnosis, stool needs to be examined.
- pork tapeworm– Similar to bull tapeworm, but shorter in length. If a person is infected with the larvae, the tapeworm will grow in his small intestine; when infected by the eggs, the larvae will migrate and can infect any organ.
- tapeworm– Their worm type is flat and can exceed 12 meters in length. People become infected by eating poorly salted caviar, dried or undercooked fish. It can colonize the small intestine for decades, constantly releasing mature fragments with larvae into the environment.
- Echinococcus- The smallest parasite in the class Tapeworms. Over the course of several years, its larvae develop cysts, which can be located in different organs and can be up to 10 centimeters or larger in diameter. Infection occurs in dogs or sick livestock. The course of the disease is characterized by distinct clinical manifestations and risk of complications.
- Cat (liver) flukes- A small worm that enters the human body by eating undercooked freshwater fish and lives in the lumen of the small intestine, bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, where it can multiply rapidly and live up to twenty years.
Although there are many types, it is possible to determine fairly accurately which worm is living in a person's body using modern diagnostic methods and an ancient proven test (worm eggs in feces).






































